REST API Intro
Getting started
To get started with Quinyx REST API, there are a few things you will need to know.
The framework used for authorizations to the REST API's is Oauth2. More detailed information can be found here https://oauth.net/2/ .
The basic flow for authentication is that a user is given a:
- uuid - this is an identifier for the set of credentials. This is to be used in communication with Quinyx support if needed.
- Client id - keep this in a safe place. Can be shared, usually used as a username in applications such as Postman or similar.
- Client secret - needs to be kept VERY confidential, this is the password and in combination with the Client id gives the owner access to the defined scopes.
- Link to be able to generate a bearer token to be used for authorizations toward the REST API
- Token is valid for 60 minutes
Different client id/ client secrets are required for our different environments
Example
To obtain a bearer token a POST call is done to https://api.quinyx.com/v2/oauth/token with the following configuration
Parameter settings (Params):
- Key = grant_type
- Value = client_credentials
Authorization
- Type = Basic Auth
- Username = Client id
- Password = Client secret
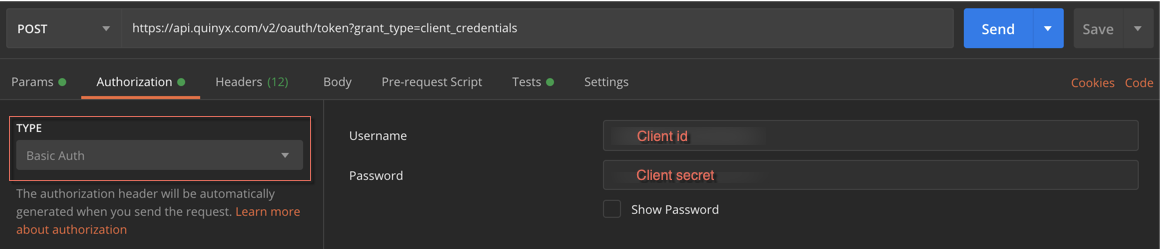
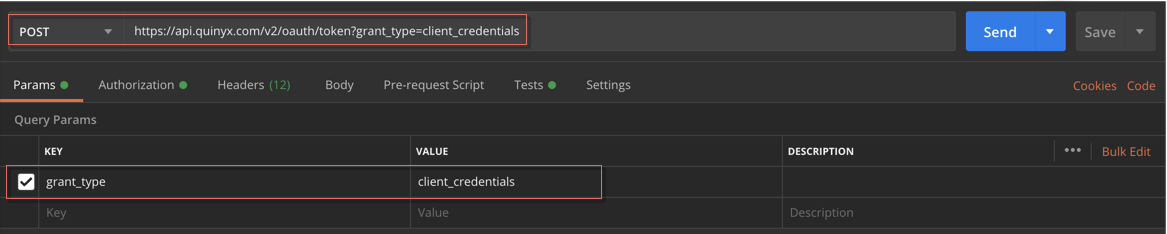
examples from Postman
Environments
RC
RC is our customer environment (Release Candidate) where you as a customer can access your data in a sandbox environment. It will contain your customer data from the production environment up until last month. The data in this environment gets updated on the evening of the 1st of each month with data from production and that will overwrite all changes made in the RC environment.
Api-docs : https://api-rc.quinyx.com/v2/docs
Quinyx RC Web Interface: https://web-rc.quinyx.com
Production
This is the production (live) environment which is reached through
Api-docs : https://api.quinyx.com/v2/docs
Quinyx Prod Web Interface: https://web.quinyx.com
Programs for testing
For testing and troubleshooting, we suggest using SoapUI or Postman, our example queries and responses are from Postman. If in contact with Quinyx always attach the request and response in .xml , .txt or similar format.
Limitations
The following limitations currently apply:
- You are not allowed to use more than 5 concurrent requests (eg. running more than 5 threads simultaneously per unique customer regardless of endpoint).
- When using GET/calculated-variables/{extCalculatedVarId} we do not currently support the retrieval of calculated variables that include standard variables in their calculation. This will be supported in a future version.
- Standard variables are currently not accessible through API:s.
TLS
All communication with Quinyx products is encrypted using TLS. To ensure all communication stays secure and your customer-data is protected Quinyx does not support any TLS protocol below version 1.2.
You can use our website https://check.quinyx.com to verify your browser
Ciphers and TLS-versions will be applied.
Quinyx API-Calls and web: TLS 1.2 with the following ciphers:
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
Quinyx Images and assets: TLS 1.2 with the following ciphers:
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
AES128-GCM-SHA256
AES256-GCM-SHA384
AES128-SHA256

